Discovery
This frame allows polling more information from an Appliance.
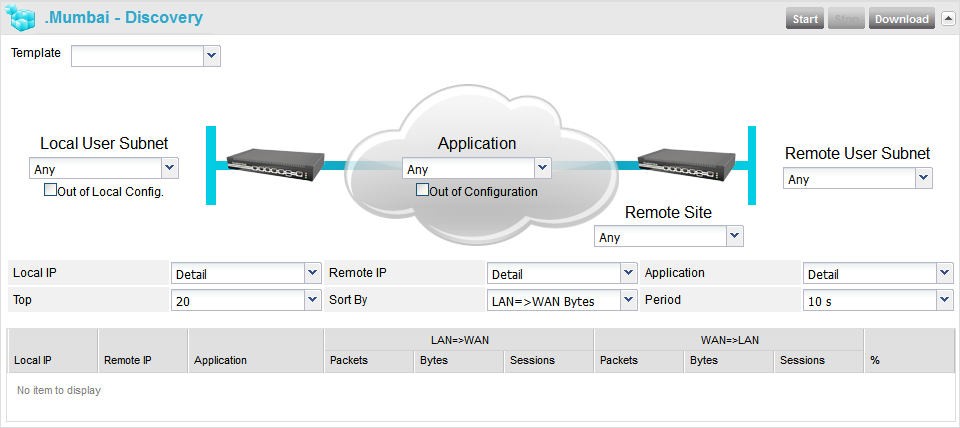
The Discovery function consists in creating a Discovery agent for the selected Appliance (one agent maximum per Appliance)
to collect additional data (as compared to the data already collected and
displayed in the Real Time Flows list see above).
To use the Discovery function:
|
2
|
Start the Discovery agent |
|
4
|
Stop the Discovery agent |
Filters
The flows can be filtered according to multiple criteria, using the
5 drop-down lists and 2 check boxes surrounding the network diagram:
|
•
|
Template: three templates can be used to filter: |
|
•
|
Out of local subnets: (= out of local config) packets crossing the Appliance, but where neither the source IP address
nor the destination IP address belong to one of its Topology subnets (this
traffic is called in Transit); these flows are not measured individually by the Appliance; instead, only their global volume is measured and reported (i.e.,
these flows are not present in the Real Time Flows list nor in any report,
except in the Site Analysis reports, which show the volume of Transit
traffic). |
|
•
|
Unrecognized Application: packets belonging to applications which are
not recognized by the Appliance's syntax
engine, which were not declared and
which do not use well-know ports, |
|
•
|
Out of Domain: sent packets with a destination IP address which does
not belong to a declared Topology subnet, or received packets with a source
IP address which does not belong to a declared Topology subnet (in either
case, these packets will match Out of Domain Topology subnet
which is in the system by default, so it does not have to be declared
, 0.0.0.0/0). |
|
•
|
Local User Subnet: to filter the data using a User subnet declared for the local Site, |
|
•
|
An Out of Local Config. check box allows, if checked,
to display the traffic which does not belong to the local configuration only
(see Out of local subnets above) |
|
•
|
Remote User Subnet: to filter the data using a User subnet declared
for a remote Site, |
|
•
|
Remote Site: to filter the data using a User subnet declared for a remote Site, |
|
•
|
Application: to filter the data according to one application, |
|
•
|
An Out of config check box, allows, if checked, to discover
the port number used by the unrecognized applications (see above). |
Start/stop a Discovery agent
A Discovery agent can be started
or stopped with the  and
and  buttons at the right of the <Site> - Discovery frame header:
buttons at the right of the <Site> - Discovery frame header:
Note: If the Start button is greyed  and the Stop button is visible
and the Stop button is visible  ,
it means that a Discovery agent is running
on the Appliance. Discovery agents consume resources, and they are not meant to run
permanently. So when you have found what you were looking for thanks to a Discovery agent, do not forget to stop it.
,
it means that a Discovery agent is running
on the Appliance. Discovery agents consume resources, and they are not meant to run
permanently. So when you have found what you were looking for thanks to a Discovery agent, do not forget to stop it.
Result table
According to the configuration rules, this Discovery agent will collect the following data and send them to the Application Configuration server:
|
Local IP
|
local IP address
|
|
Remote IP
|
remote IP address
|
|
Application
|
name of the application, displayed as follows:
|
•
|
when
the application is recognized: A (b), where A
is the declared name and b
is the application recognized by the syntax engine: |
|
•
|
for a standard
application (e.g. FTP) it reads: FTP (ftp), |
|
•
|
for
an application with a specific declaration (e.g. Ping_X is declared as follows: protocol: ICMP; User subnet:
X), it reads: Ping_X (icmp) |
|
•
|
for an application which
is not recognized by the Appliance' syntax
engine, but which is declared,
it reads: <Application_name> (unknown) |
|
•
|
when the
application is not recognized (it is not recognized by the Appliance and it has not been defined), it displays the layer 4 protocol and the port number. |
|
|
LAN => WAN Packets
|
number of ingress packets
|
|
LAN => WAN Bytes
|
number of ingress bytes
|
|
LAN => WAN Sessions
|
number of ingress sessions
|
|
WAN => LAN Packets
|
number of egress packets
|
|
WAN => LAN Bytes
|
number of egress bytes
|
|
WAN => LAN Sessions
|
number of egress sessions
|
|
%
|
percentage of traffic that each line represents over the total, in
terms of LAN=>WAN Packets, LAN=>WAN Bytes, LAN=>WAN Sessions, WAN=>LAN Packets,
WAN=>LAN Bytes or WAN=>LAN Sessions, according to the Sort by
choice
|
Note: The counters are cleared at each start of a Discovery agent.
The result can be downloaded in CSV format by clicking on the  button
at the right of the <Site> - Discovery frame
header.
button
at the right of the <Site> - Discovery frame
header.
Display settings
The results can be displayed in different ways, thanks to 6 drop-down
lists below the network diagram:
|
•
|
Detail: the local IP addresses are displayed (so different local IP
addresses will always be displayed on different lines), |
|
•
|
Group: the local IP addresses are not displayed (and all flows with
the same remote IP address and same application will be merged on one line,
even if they have different local IP addresses). |
|
•
|
Detail: the remote IP addresses are displayed (so different remote IP
addresses will always be displayed on different lines), |
|
•
|
Group: the remote IP addresses are not displayed (and all flows with
the same local IP address and same application will be merged on one line,
even if they have different remote IP addresses). |
|
•
|
Detail: the application names are displayed (so different applications
will always be displayed on different lines), |
|
•
|
Group: the application names are not displayed (and all flows with the
same local IP address and same remote IP address will be merged on one line,
even if different applications are running between these two addresses). |
|
•
|
20: shows the 20 most significant results (in Packets, Bytes or Sessions,
according to the field used to sort the data), |
|
•
|
50: shows the 50 most significant results, |
|
•
|
100: shows the 100 most significant results. |
|
•
|
Sort by: it is possible to sort the data according to the number of: |
It is also possible to sort the data by clicking on the column headers.
|
•
|
10 s: the results are refreshed every 10 seconds, |
|
•
|
1 mn: the results are refreshed every minute, |
|
•
|
5 mn: the results are refreshed every 5 minutes. |
 and
and  buttons at the right of the <Site> - Discovery frame header:
buttons at the right of the <Site> - Discovery frame header:
 and the Stop button is visible
and the Stop button is visible  ,
it means that a Discovery agent is running
on the Appliance. Discovery agents consume resources, and they are not meant to run
permanently. So when you have found what you were looking for thanks to a Discovery agent, do not forget to stop it.
,
it means that a Discovery agent is running
on the Appliance. Discovery agents consume resources, and they are not meant to run
permanently. So when you have found what you were looking for thanks to a Discovery agent, do not forget to stop it. button
at the right of the <Site> - Discovery frame
header.
button
at the right of the <Site> - Discovery frame
header.