Configuring a multi-ip|engine Branch Office Site through VRRP
This section describes how to configure a Branch Office Site with two ip|engines having the same AS in the same subnet, through VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol). The objective of this deployment is high availability, i.e. if the master ip|engine is in bad health, the other ip|engine is used as backup ip|engine.
Warning: VRRP deployment is not supported for a Branch Office Site with two full router ip|engines in multipath mode.
Graph legend
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grey connection |
|
ip|engine |
router |
switch |
subnet |
host in a subnet |
server |
connection between devices |
Note: A router may be a CE Router (MPLS Router), an Internet Access Router or a Core Router.
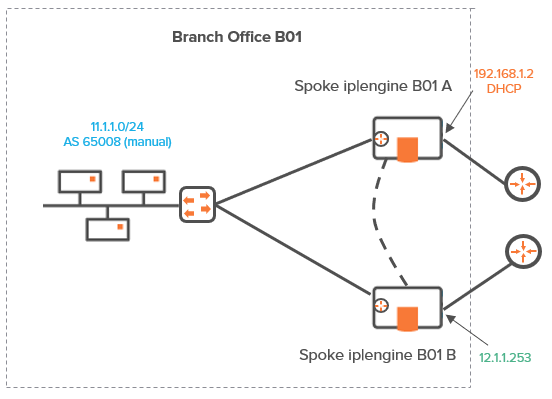
Since the following Use Case is complementary to "Use Case 2", there is one prerequisite which is the necessary configuration of the second spoke ip|engine for Branch Office 1. For detailed explanations, refer to "Configuring the Branch Office ip|engines".
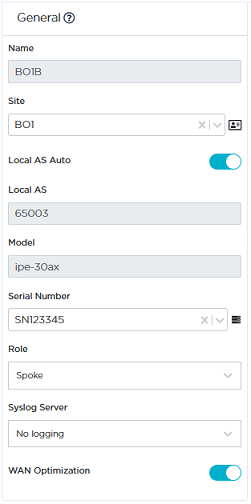
| 1 | Identify this spoke ip|engine as follows: |
| 2 | Configure its LAN as follows: |
| • | Click the Interfaces tab. |
| • | Enter the ip|engine Management IP Address (11.1.1.6), Prefix Length (24). The Management IP address is used for communicating with other ip|engines, the ZTP Server and the Orchestrator. |
Note: Since the three IP addresses directly following the Management IP address (11.1.1.2) of the B01 first ip|engine are used for its WAN routers, enter 11.1.1.6 as the Management IP Address of the second ip|engine.
| • | Use the default Auto Generated option (creation window only) to let the system allocate LAN addresses automatically to the Routers (Router X IP = Management IP + X) linked to the WANs that you configured for this ip|engine. Also refer to "IP Address allocation". |
In this example, Router 1 IP address will be automatically defined as it corresponds to WAN1.
| • | Enable the DHCP Relay function and enter the DHCP Server Address (11.1.4.250). DHCP requests from the B01B ip|engine are propagated to the DHCP Server in the Data Center LAN. |
| • | Do not enter any VLAN ID. Note that the grey values appearing in some fields of the interface are only given as examples and are not taken into account in the configuration. |
| • | Do not define any Subnets. |
| 3 | Define its WAN1 interface as follows: |
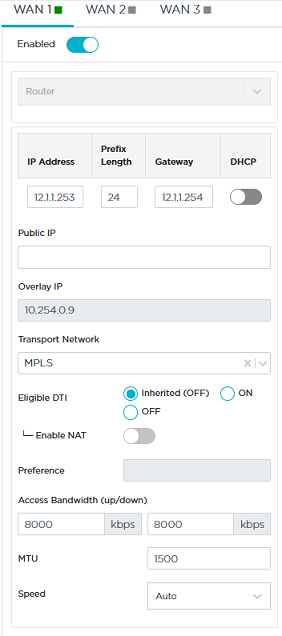
| 4 | Then define the VRRP parameters of the B01B ip|engine to enable high availability between the two spoke ip|engines as illustrated in "Use Case 6" diagram. |
| • | On the LAN panel, enable VRRP. |
| • | Enter the VRRP Virtual router IP address: 11.1.1.10 |
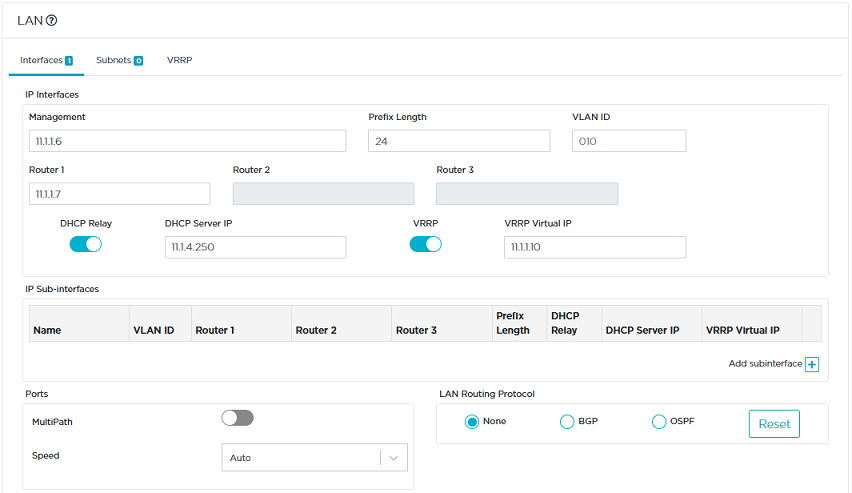
| • | Click the VRRP tab. |
| • | Enter a value between 1 and 255 in the Virtual Router ID field. |
| • | Select Backup as Initial State. This means the B01B ip|engine is used as the backup machine if B01 fails. |
By default, all existing WAN interfaces are checked.
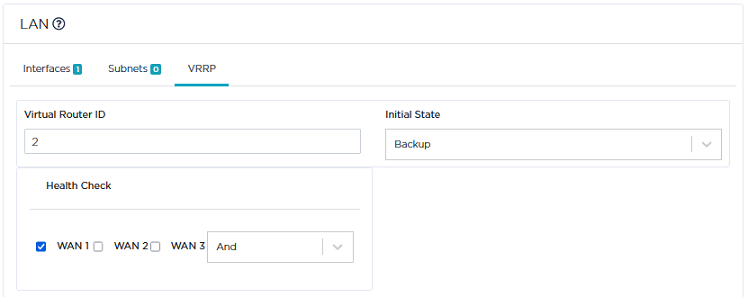
| 5 | Validate your settings by clicking the Create or Update buttons. |
| 6 | Edit B01 ip|engine. |
| • | On the LAN panel, enable VRRP. |
| • | Enter the VRRP Virtual router IP address: 11.1.1.10 |
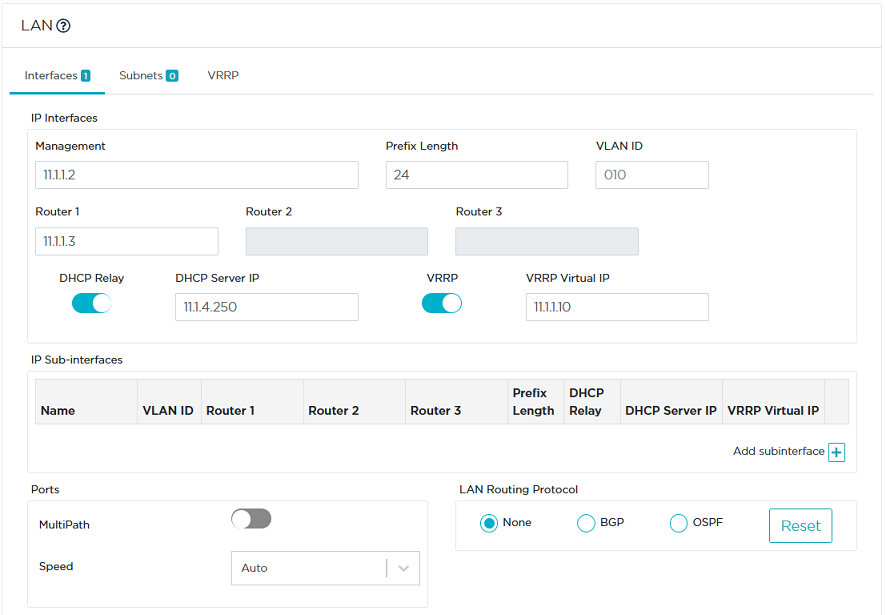
| • | Click the VRRP tab. |
| • | Enter 2 as Virtual Router ID (same ID defined for B01B). |
| • | Select Master as Initial State. |
By default, all existing WAN interfaces are checked.
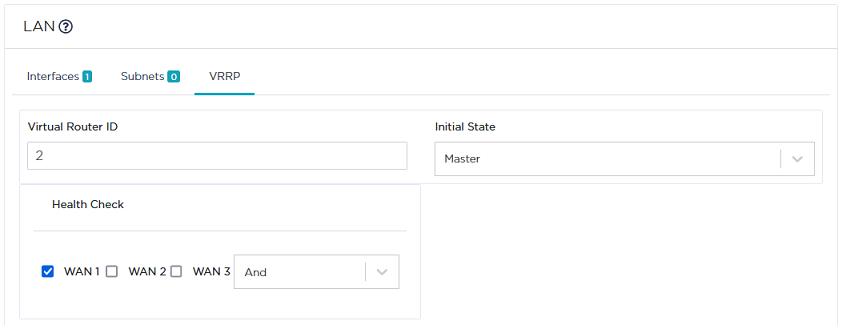
| 7 | Validate your settings by hitting the Create or Update buttons. |
| 8 | You may optionally customize the SD-WAN Orchestrator VRRP Settings through the Advanced Configuration menu. |