Hybrid Mode Standard Deployment
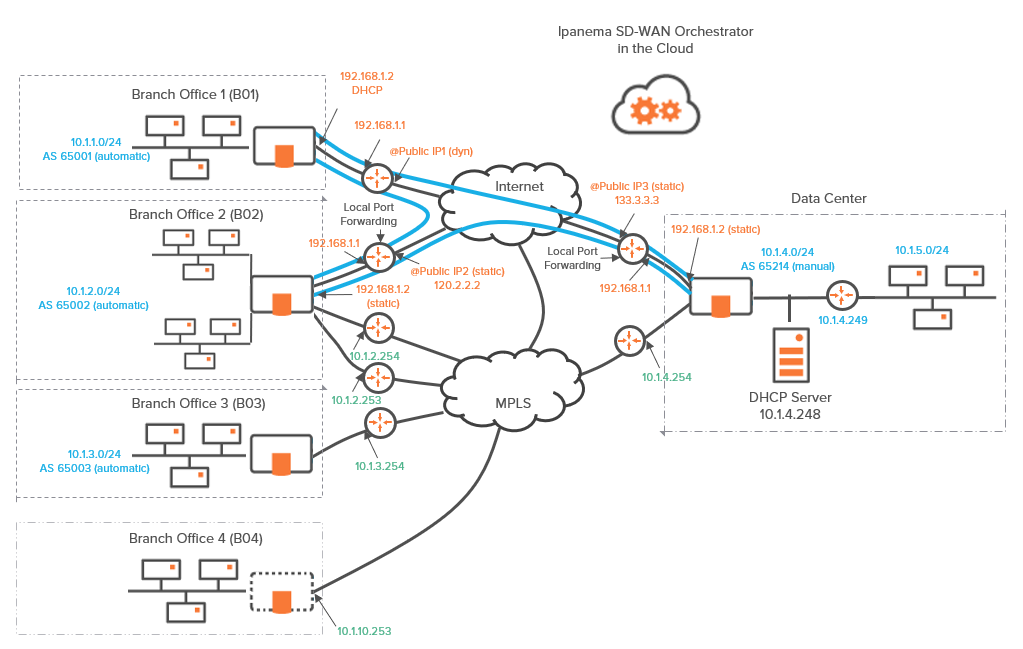
This section describes the main steps for configuring a hybrid network. It is based on a typical use case illustrating a simple deployment where three branch office ip|engines are connected to a Data Center ip|engine through/over either the MPLS private network, or over the Internet, or both. This deployment consists of configuring the ip|engines.
| • | B01 is deployed in router mode and is connected to the Data Center through one tunnel over the Internet. |
| • | B02 is deployed in bridge/router mode with a multi-path LAN. It is connected to the Data Center directly through MPLS and over the Internet via one tunnel. A third tunnel connects B02 to B01. |
| • | B03 is deployed in bridge mode and is connected to the Data Center through the MPLS private network. |
| • | B04 is tele-managed by remote ip|engines. |
"Configuring the Data Center ip|engine"
"Configuring the Branch Office ip|engines"
Graph legend
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
Blue connection |
Grey connection |
|
ip|engine |
router |
tele|engine |
subnet |
host in a subnet |
server |
IPsec tunnel |
physical connection between devices |
Note: A router may be a CE Router (MPLS Router), an Internet Access Router or a Core Router.
Configuring the ip|engines
To configure your network ip|engines, select Network -> Configuration from the Orchestrator main menu.
You generally configure an automatically provisioned ip|engine. In some specific cases, you may also configure an ip|engine which is still undefined on the ZTP Server. Refer to "Identifying the ip|engine".
A tele|engine is a ghost ip|engine which is never provisioned on the ZTP Server. Refer to "Configuring the B04 Branch Office tele|engine".
Note: a virtual|engine is managed as a physical ip|engine by the SD-WAN Orchestrator.
The basic procedure for defining an ip|engine consists of the following steps:
| • | Identifying the auto-provisioned ip|engine |
| • | Configuring the LAN |
| • | Configuring the WAN |
In Use Case 1, you first configure the Data Center ip|engine, and then the three other branch office ip|engines (B01, B02 and B03). You may also configure a branch office tele|engine, B04.
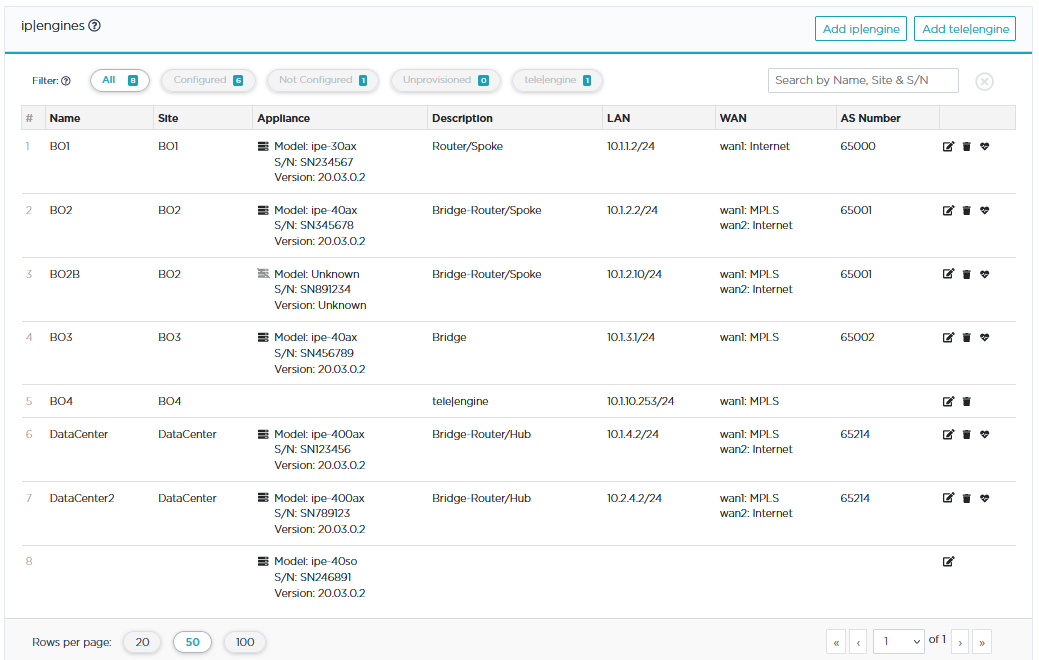
The Network -> Configuration window lists the ip|engines of your network. You may filter them in several ways.
| • | Configured: these ip|engines are provisioned and totally configured. They are operational in your network. |
| • | Not Configured: the ip|engines have been automatically provisioned in the SD-WAN Orchestrator from the ZTP Server. They are only visible through their Serial Number and must be further identified and configured. |
| • | Unprovisioned: though these ip|engines are displayed and configured, they are not defined on ZTP and consequently are not operational in your network. |
| • | tele|engine: though these ghost ip|engines are displayed and configured, they are never defined on ZTP and are managed by operational remote ip|engines. |
Note that:
| • | the |
| • | the |
| • | the |
Searching for an ip|engine
You can look for an ip|engine by typing its Name, Site or Serial Number in the Search field. Click the  button to delete the Search filters. Note that the Status filters adapt to the search results.
button to delete the Search filters. Note that the Status filters adapt to the search results.
List Navigation
When the Network -> Configuration window contains several thousands of ip|engines, the navigation functions at the bottom of the window enable you to navigate through the list.
| • | By default, one page includes 50 rows. 20 and 100 are the other options. |
| • | The total number of pages is specified (24 in the example below). This number changes if you select a different number of rows per page. |
| • | You can display a particular page by directly selecting it from the stack or by clicking the  and and  buttons to move from one page forward and backward. buttons to move from one page forward and backward. |
| • | Click  to view the first page and to view the first page and  to view the last page of the list. to view the last page of the list. |
Modifying, replacing or deleting an ip|engine
| • | Click  to save your settings. to save your settings. |
Replacing an ip|engine
Warning: When replacing an ip|engine by another one, NEVER delete the ip|engine to be replaced in the SD-WAN Orchestrator because its configuration will be lost.
If the ip|engine is auto-provisioned:
| 1 | Your system administrator deletes it on the ZTP Portal; the deleted ip|engine is listed as 'Unprovisioned' in the SD-WAN Orchestrator. |
| 2 | In the Network -> Configuration list, edit the unprovisioned ip|engine (which is still configured) and enter its new Serial Number. |
| 3 | Update the configuration. |
| • | Click |
| • | Click |