Configuring traffic redirection to an External Gateway
The purpose of this Use Case, which is complementary to "Use Case 1", is to enable access to a site where there is no ip|engine. This section describes how to configure an external gateway from Branch Office 2 ip|engine over the Internet.
One tunnel is created after you have defined the appropriate parameters in both the Orchestrator and in Microsoft Azure.
Note: Only Microsoft Azure and Cisco devices are supported in this SD-WAN Orchestrator version.
"Defining the External Gateway and Routing parameters"
"Connecting the Branch Office ip|engine to the Gateway"
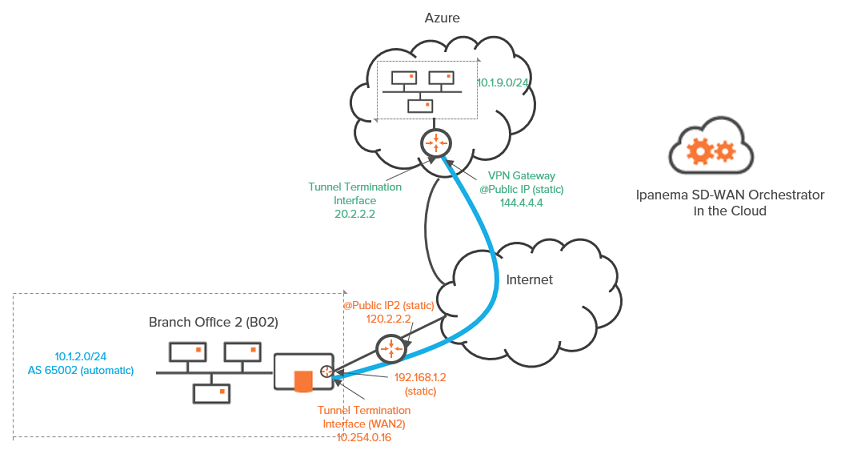
Graph legend
|
|
|
|
|
|
Blue connection |
Grey connection |
|
ip|engine |
router |
subnet |
host in a subnet |
server |
IPsec tunnel |
physical connection between devices |
Note: A router may be a CE Router (MPLS Router), an Internet Access Router or a Core Router.
Creating an external gateway
Select Network -> External Gateways from the Orchestrator main menu.
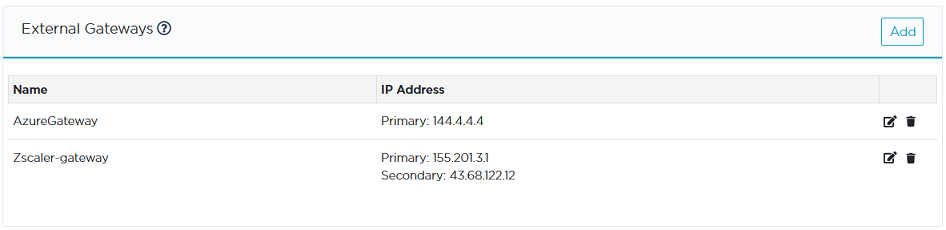
On the displayed window, click the Add button to display the form. The basic procedure for defining an external gateway consists of the following steps:
| • | Identifying the external gateway |
| • | Defining the Public IP addresses of both the VPN Gateway and the Branch Office ip|engine it is connected to. The IP addresses of the tunnel termination interfaces are also required. |
| • | Defining how the traffic is routed through the tunnel by using subnet information (static configuration) or BGP (dynamic configuration). |
| • | Defining the IPSec tunnel parameters. |
Refer to the following sections for detailed explanations.
Modifying or deleting an external gateway
| • | Click  to save your settings. to save your settings. |
| • | Click |